Feminized seeds are the Wonder Woman of the cannabis world - strong, powerful, and all-female.
Whether you're a commercial grower or a home gardener, feminized seeds offer a number of advantages. By inducing female plants to produce seeds without being pollinated by a male, you can ensure that your plants will be all-female, which means you won't have to worry about any male plants sneaking in and ruining your crop.
Feminized seeds are made by forcing a plant to create pollen that only contains female X chromosomes. This pollen is then used to pollinate a female plant resulting in seeds that only contain the female genes.
Read along to learn more. It's worth it.
What are female cannabis seeds?
Female cannabis seeds are from the female cannabis plant that have not been fertilized by male pollen.
Only female cannabis plants produce the sought-after flowers or buds, which contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD. This makes them valuable for medicinal and recreational use.
Cannabis plants, like many other plants, reproduce through sexual reproduction. Female cannabis plants produce flowers with pistils, which are the reproductive organs that contain ovules. When the female plants are pollinated by male cannabis plants, they produce seeds.
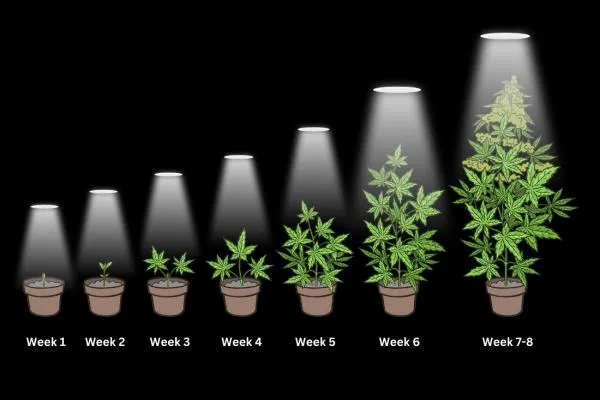
Buying feminized seeds ensure that virtually all plants grown from these seeds will be females, eliminating the risk of pollination and seed production. This allows growers to focus on producing high-quality flowers with optimal cannabinoid content. Female cannabis seeds have become popular among growers because of their ability to streamline the cultivation process and enhance the yield and potency of the final product.
What are the benefits of growing feminized seeds?
Feminizing seeds is a common practice in cannabis cultivation for several reasons:
1. Guaranteed Female Plants: Feminized seeds ensure that nearly all resulting plants will be females. Since female cannabis plants are the ones that produce the cannabinoid-rich flowers, which are the primary goal for most growers, feminized seeds eliminate the risk of getting male plants that don't produce flowers.
2. Increased Crop Efficiency: By using feminized seeds, growers can maximize their crop efficiency. All female plants mean no resources are wasted on cultivating male plants that are not useful for flower production. This allows growers to focus their efforts and resources on maximizing the yield and potency of the cannabinoid-rich flowers.
3. No Pollination Risk: Female cannabis plants that are allowed to come into contact with male pollen will start producing seeds, diverting energy away from flower production. By using feminized seeds and preventing male plants from being present, growers can avoid accidental pollination and maintain the quality and potency of their harvest.
4. Consistency in Traits: Feminized seeds lead to a more uniform crop in terms of growth characteristics and cannabinoid content. This consistency is valuable for commercial growers who seek predictability in their yields and products.
5. Time and Space Savings: Cultivating male plants alongside females takes up valuable space and resources. Eliminating male plants through the use of feminized seeds allows growers to use their growing space more efficiently and harvest more usable flowers in the same amount of time.
6. Breeders' Tool: Feminized seeds are also useful for breeders who want to produce stable, true-breeding strains. By crossing two feminized plants with known traits, breeders can create offspring that are more likely to exhibit desired characteristics.
It's important to note that feminized seeds are created through various methods, such as stressing female plants to produce male flowers (from which pollen is collected) or using specific breeding techniques to produce seeds that are more likely to be female.
While feminized seeds offer advantages for commercial growers and breeders, some traditionalists may prefer working with regular seeds that include both male and female plants as they believe in preserving the natural genetic diversity of the cannabis plant.

The different ways of creating female seeds
Creating female seeds, also known as feminized seeds, involves various techniques to ensure that the resulting plants are predominantly female.
The goal is to produce seeds that will yield female plants without the presence of male chromosomes. Here are the different ways of creating female seeds:
1. Colloidal Silver Method: This method involves applying a solution of colloidal silver to select female plants during the early stages of flowering. Colloidal silver contains silver particles suspended in a liquid, and when sprayed on the female plant, it disrupts ethylene production, a hormone crucial for female flower development. The plant, in response, starts producing male flowers with pollen. This pollen is then used to pollinate other female plants, resulting in seeds that will produce female plants (XX chromosomes) as they inherit two X chromosomes from the parent female.
2. Silver Thiosulfate Method: Similar to colloidal silver, silver thiosulfate is used to produce male flowers on female plants. A solution of silver thiosulfate is applied to selected branches of the female plant, causing male flowers to develop within 1-2 weeks. These male flowers are then used to pollinate other female plants, resulting in feminized seeds.
3. Gibberellic Acid: This uses hormones that naturally occur in plants known as Gibberellins to encourage the growth of male flowers in cannabis plant. Gibberellic Acid 3 is the most widely available variation that is available to buy and is the most effective.
4. Rodelization: Rodelization is a natural process that some female cannabis plants undergo when they are not pollinated. In the absence of pollination, the female plant may develop male flowers containing pollen (often known as "bananas" or “ball sacks”) late into the flowering stage as a last-ditch effort to produce seeds. These can be used to pollinate other female plants to create feminized seeds. However, this method is less reliable and can result in a higher likelihood of hermaphroditic traits in the resulting plants.
5. STS (Silver Thiosulfate and Sodium Thiosulfate) Method: This is a more refined version of the silver thiosulfate method. A precise combination of silver thiosulfate and sodium thiosulfate is used to reverse the gender of a female plant temporarily. This reversed female plant is then used to pollinate other female plants, leading to the production of feminized seeds.
6. Selective Breeding: Some breeders use traditional breeding methods to select and cross plants that have a higher likelihood of producing female offspring. Over time, through selective breeding, they can develop strains with a higher percentage of female plants.
It's essential to note that while feminized seeds are popular for their convenience and guaranteed female plants, they may carry a slightly higher risk of hermaphroditism (the development of both male and female flowers) compared to regular seeds if a hermie forcing technique is used.
Proper breeding practices and seed selection can help mitigate this risk and ensure the quality and stability of feminized seeds.
How seeds are feminized using colloidal silver:
To feminize seeds using the colloidal silver method:
1. A solution of colloidal silver is prepared. Colloidal silver is available commercially or can be made by suspending silver particles in water.
2. The colloidal silver solution is applied to parts of selected female cannabis plants during their early flowering stage. This can be done through spraying or brushing the solution onto the plant's branches or flowers until it drips off.

3. Immediately put the plant into 12/12 light/dark to promote flowering. After 1-2 weeks male flowers will develop. As the application of colloidal silver disrupts the plant's natural hormonal balance, causing it to develop male flowers (pollen sacs) instead of female flowers.
4. The pollen from these male flowers is carefully collected and used to pollinate other female cannabis plants. The resulting seeds from this pollination will be feminized, meaning they will have a high likelihood of producing female plants.
Which method is best? Colloidal Silver Method or Rhodelization (Selfing)
This a tricky question, but here are the pros and cons of each method to give you an idea:
Colloidal Silver Method:
Pros:
- Reliable and predictable: The colloidal silver method is a more controlled approach, ensuring a higher success rate in obtaining feminized seeds.
- Faster results: The process of feminization using colloidal silver is relatively quick, providing faster seed production.
Cons:
- Requires additional materials: Acquiring or making colloidal silver may involve extra effort and cost.
- Potential chemical exposure: Working with colloidal silver requires caution, as it involves handling a chemical solution.
Rhodelization (Selfing):
Pros:
- Natural process: Rhodelization occurs without the use of chemicals, making it a more natural approach.
- No need for additional materials: No external substances are needed for the self-pollination process.
Cons:
- Lower success rate: Rhodelization is less reliable than the colloidal silver method, resulting in a lower percentage of feminized seeds.
- Slower process: It may take longer for the plant to undergo rhodelization and produce male flowers for self-pollination.
How you can make your own colloidal silver
Making colloidal silver at home involves a simple process that requires a few basic materials. Here's a general guide on how you can make your own colloidal silver:
Materials Needed:
1. Pure silver electrodes or silver wire (99.99% pure is recommended)
2. Distilled water
3. Glass container (preferably dark glass to minimize light exposure)
4. DC power supply or batteries (9V batteries work well)
Step-by-Step Process:
1. Prepare the Setup: Clean the glass container thoroughly to ensure it's free from any contaminants. Fill it with distilled water, leaving enough space for the silver electrodes to be submerged.
2. Attach the Electrodes: Insert the pure silver electrodes or silver wire into the water, ensuring that they do not touch each other. The electrodes should be immersed but not completely submerged in the water.
3. Power the System: Connect the silver electrodes to the DC power supply or batteries. The positive electrode (anode) should be connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, while the negative electrode (cathode) should be connected to the negative terminal.
4. Monitor the Process: Turn on the power supply or connect the batteries. You should observe a very faint silver color or cloud forming around the negative electrode. This cloudiness is the colloidal silver particles being produced.
5. Timing: The time required for colloidal silver production varies depending on the power output and the concentration desired. As a general guideline, it may take several hours to produce a colloidal silver solution with optimal particle size.
6. Safety Precautions: While this process is relatively simple, it's essential to take safety precautions. Avoid using high voltage as it can lead to the production of larger silver particles, which are less desirable for colloidal silver. Also, ensure that the electrodes do not touch each other to prevent short-circuiting.
7. Storage: Once the colloidal silver is ready, turn off the power supply and carefully remove the electrodes. Store the colloidal silver solution in a dark glass container away from direct light to maintain its effectiveness.
It's important to note that making colloidal silver at home may not yield the same consistency or concentration as commercially available products. Commercially produced colloidal silver undergoes rigorous quality control and testing to ensure purity and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Feminized seeds are created in a variety of methods. Using chemicals such as Colloidal silver is the most popular, but by inducing stress on female cannabis plants to produce all-female offspring is another more "natural" approach, ensuring plants with bigger yields and no worries about male plants.
By understanding this process, growers can confidently select and cultivate feminized seeds for their next grow, boosting productivity and efficiency.