Marijuana plant anatomy is an important thing to know for growers and breeders.
Marijuana plants may have different anatomy depending on their sex. Cannabis plants are typically either male or female, just like humans. However, they can also be hermaphrodites. This means they have both male and female reproductive parts. These parts are important to know, as determining sex early can save an entire crop from being pollinated. And knowing which parts to train can also result in bigger, frostier buds from any female plant. When cloning, it’s also important to know marijuana plant anatomy so that a clipping can be taken from a plant without destroying it.
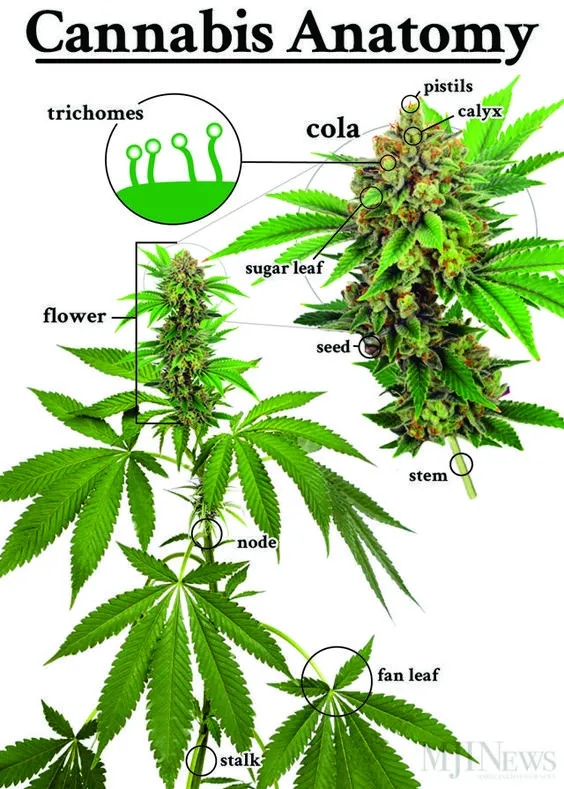
Marijuana Plant Anatomy
Roots
As mentioned, there are many parts of a marijuana plant that are common to both male and females. Roots are one of them. These are essentially the lifeline of the marijuana plant. When the roots are not healthy, the entire plant will suffer. Roots take nutrients and water from the grow medium and deliver it to every part of the plant.
Cannabis roots are long and fibrous. There is one primary root, known as the tap root and secondary roots grow all around it.
Stems
The main stem grows from the primary root and then stalks and leaves from there. The stem works with the roots as part of the transportation system. In addition, the stem also acts as the main support for the entire plant. This allows other stalks and leaves to grow up and out, so the plant can reach its full growth potential.
Nodes and inter-nodes
Along the stem are nodes, a very important part for marijuana plant anatomy. Nodes are the points of the stem where other branches will shoot out from. These are important to not only get larger plants, but also for those that want to clone or train their plants. Cutting and training is often done very close to the node. Therefore, it is important that anyone wishing to cultivate marijuana knows where those nodes are. The spaces between these nodes also have a name of their own and are known as inter-nodes.
Stipules
When a new node is formed a stipule may also be produced. In other plants, such as roses, these stipules often grow in the form of thorns. These protect the plant from things such as pests. In the marijuana plant however, they do look like a small dagger but are harmless. In fact, the stipule is one part of the plant in which no one really knows its purpose.
Fan Leaves
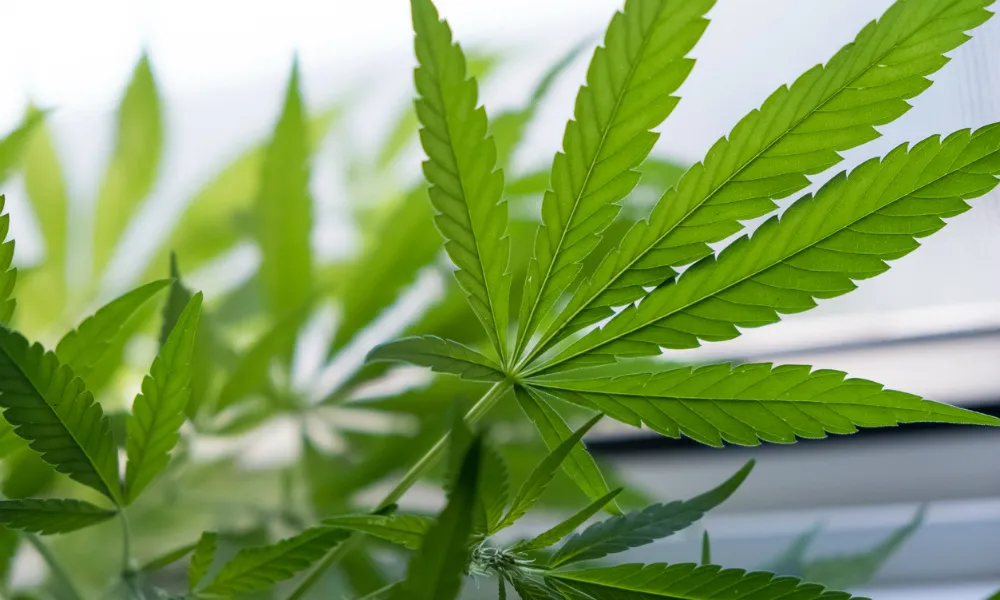

Every marijuana plant, whether male or female, is going to have leaves. Leaves are a backbone of any weed plant. Leaves play a very important role in marijuana plant growth. Weed leaves absorb all of the light the plant is exposed to and even some moisture in the air. Through the process of photosynthesis, they also deliver all those nutrients to the rest of the plant.
Weed leaves can also be defoliated. This means the leaves can be removed at some points during the growth process. This is done when there are many fan leaves. Removing some of them allows light and air to better circulate around the plant. This can result in bigger yields and a healthier plant. As well as decreasing the chances of getting bud rot and mould.
On the top and bottom of each leaf are stomata. This literally means “mouth” in Greek. These stomata open and close, depending on conditions. The stomata may close in order to prevent the plant from becoming waterlogged. When the plant is dry, it may open the stomata fully, in order to absorb as much water as possible.
We can learn a lot from the appearance of cannabis leaves, such as what type of cannabis variety the plant is to its condition of health. Indica leaves are typically fatter and wider, whereas sativa leaves are much longer and thinner.
Female and Male Marijuana Plants.
Female and Male marijuana plants share most of the same parts. However, the reproductive parts are very different. And females have many more of these than their male counterparts.
Bract and Calyx
The bract contains the reproductive parts of the female. They are green, shaped like teardrops and heavily covered in resin glands. Inside the bract and invisible to the naked eye is the calyx. This is a small layer covering the ovule at the base of the flower.
Stigma and Pistil
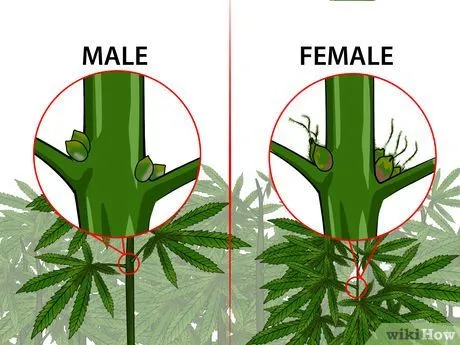
Two very important parts of the female marijuana plant anatomy are the stigma and the pistil. The pistil is the main reproductive part of the female part and it is covered with stigmas. These stigmas look like little hairs. The female plant hopes that by shooting these pistils out, it will be fertilized by a male plant. At that time, it will produce seeds.
However, this is what many growers try to avoid. When the female is fertilized by the male plant, there will be no buds, therefore it is vital to understand how to sex cannabis plants early on. That will only happen when the female does not get fertilized and instead, focuses on producing flowers, or buds.
Colas
As those buds grow, they will grow tightly packed in a bundle together. Those bundles are known as colas. While there can be many throughout a plant, the main cola sits at the very top.
Trichomes
Within that cola will be many buds that are covered in trichomes. These are present genetically to protect the plant against pests. However, people today mostly know them for containing a high amount of cannabinoids. Particularly THC which increases the effects of the plant when consumed.
Pollen Sacks
Pollen sacks can only be found on the male marijuana plant and important for breeding. Instead, they have anthers, which are pollen sacs held onto the stem by a filament. In its entirety, these reproductive parts are known as the stamen.
The pollen sacs on a male plant are small, measuring at about five millimeters. They look like a small ball or egg. When the male plant reaches maturity, these sacs will burst open and sending pollen through the air to any nearby female plants. This is good for breeders that are using two strong parent plants to create seeds. It is not good however, for growers looking to produce gorgeous buds. Growers can sex their marijuana plants when they enter the flowering stage and remove male plants from the grow area.
Understanding marijuana plant anatomy is important for anyone that is growing marijuana.
Perfectly healthy plants can turn hermie either through genetics, or due to stress during the growing stage. It is typically recommended that hermie plants are destroyed, as they can self-pollinate turning the entire plant to seed. Due to its genetics, this seed will likely be useless, as it will only produce more hermies.
You'll be able to sex your plants easily when they enter the flowering stage. And it’s at that time that growers and breeders can decide what they want their plants to be used for.