Phosphorus - the quiet, almost unassuming powerhouse of plant nutrition.
It fuels cannabis growth at every stage, from sturdy roots to resin-dripping buds. When deficiency strikes, leaves darken, growth slows, and potency can drop. And with most cannabis nutrient deficiencies often moonlighting as, or at least sharing, symptoms with other common weed cultivation issues (like nutrient lockout, light stress, and disease) - it can be tough to know exactly what the hell is going on.
Here, I show you exactly how to spot, treat, and (perhaps most importantly) prevent phosphorus deficiency, so your next crop is one to write home about.
Understanding phosphorus deficiency in cannabis
What is phosphorus deficiency?
All plant life needs access to a pretty wide range of nutrients. They're split up into two main groups - macronutrients and micronutrients. Micronutrients are only needed in small amounts (like iron, boron, calcium, and magnesium), while macronutrients make up the bulk of your crop's diet.
The big 3 macros are:
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Potassium (K)
Now, you may be thinking that a phosphorus deficiency is caused by a lack of...well, phosphorus.
While this can be true, it's often a little more complicated than that...
Why is phosphorus important for cannabis plants?
Phosphorus is the 'jack of all trades' when it comes to plant growth and development. It's a key ingredient in:
- Photosynthesis
- Energy production
- Cell division and growth
- Root development
- Flowering and fruiting
When a plant starts to struggle to uptake enough phosphorus (for whatever reason), it can cause a whole heap of problems. Plants use phosphorus at every stage of growth - which means that even a slight deficiency can really impact cannabinoid and terpene production.
Causes of phosphorus deficiency in cannabis
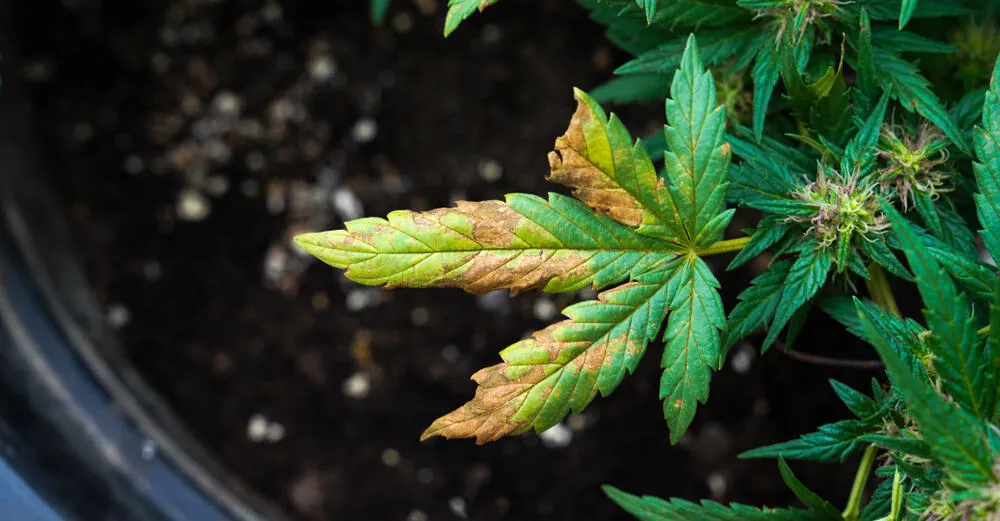

Common reasons for phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants
So, this is where we get into the weeds a little.
All cannabis deficiencies, phosphorus included, can be caused by a bunch of different issues. The most common (especially for those among us growing with a hydroponic setup or with coco-coir as the main substrate) is a pH imbalance, not an actual lack of phosphorus.
How pH levels affect phosphorus absorption
For weed plants to be able to actually take in/use the nutrients in their medium (soil, coco-coir, clay balls), they need to be within a specific pH range.
While each strain has a very slightly different pH, for the most part, cannabis will be like a soil-based medium between 6.0 and 7.0. For hydroponic setups, a slightly lower pH of 5.5 to 6.5 is ideal.
If the pH isn't within this range, it can make it difficult for your cannabis plants to absorb phosphorus (as well as all other nutrients). This can lead to a deficiency even if there are adequate levels of phosphorus in the soil or nutrient mix.
Over-watering
The absolute most common mistake new growers make is overwatering their crop.
Overwatering can cause a number of nasty issues (think root rot, fungus gnats, and spider mites), but it can also deprive your weed plants of vital nutrients.
When you overwater, all the oxygen in the soil is pushed out by water, making it difficult for the roots to "breathe". This means that even if there is enough phosphorus available in the medium, your cannabis plants won't be able to absorb it properly.
Environmental factors impacting phosphorus uptake
Colder than optimal root zone temperatures (below around 59°F/15°C) can also cause a phosphorus deficiency. If your growing substrate is cold, your roots will be, too, and when the temperature drops, the uptake of phosphorus can slow down.
Poor growing media aeration is also a huge issue. It's not just overwatering that can cause this, but also a general lack of drainage.
Poor-quality soil or nutrients
Surprisingly, this is actually the least common cause of phosphorus deficiency. Most reputable soil and nutrient companies will have a good balance of all essential nutrients for your weed plants, and most new growers these days like to take advantage of all the amazing, cannabis-specific soil blends and off the shelf nutrient options out there.
It's still worth keeping in mind, though - as it can happen, especially if you are using sub-par soil or nutrients.
Identifying signs and symptoms of phosphorus deficiency
Visual signs of phosphorus deficiency in leaves and stems
Working out what's wrong with your precious weed plants isn't always easy, especially if you're new to growing. Visual cues are the first place to start, but it also depends on how old your plants are and what stage of growth they're in.
Vegetative stage
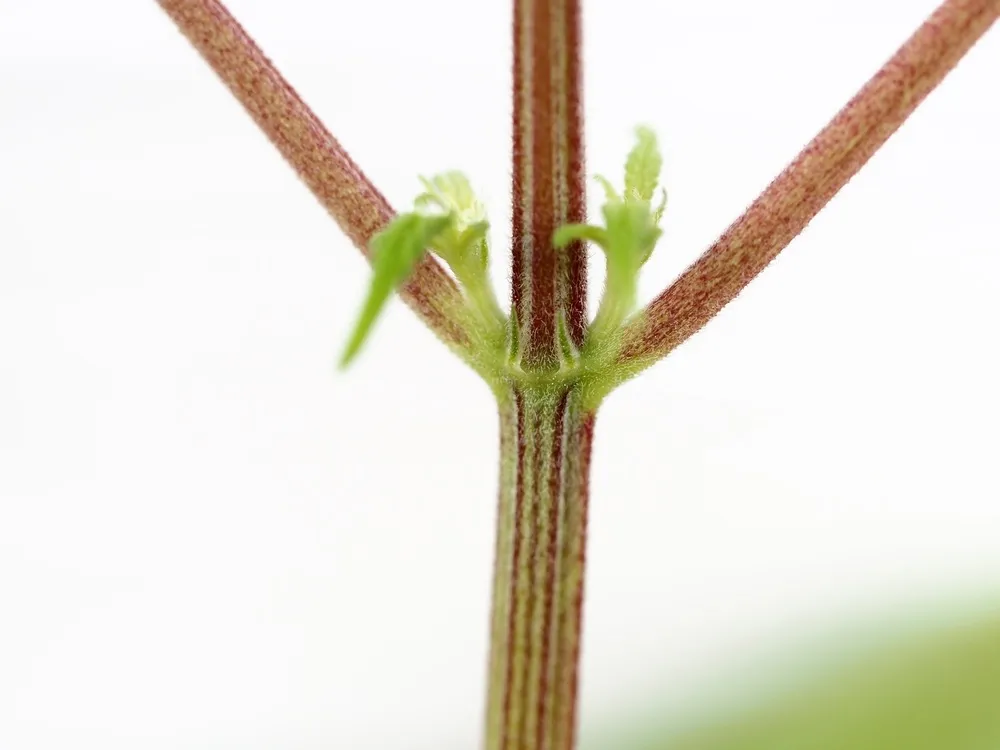

If your plants are still in the vegetative growth stage and have severely slowed down outward growth, have dark (but not burnt) leaf tips at the top of the cannabis plant's canopy, and have reddening stems and leaves - chances are you're looking at a phosphorus deficiency.
The symptoms in the vegetative stage are usually less obvious than they are later on, which can make spotting nutrient deficiencies more difficult. If you're noticing wilting leaves or stunted growth, it's definitely worth doing a little more investigation.
Flowering stage

Once your cannabis plants have started to flower, visual cues for phosphorus deficiency become much more apparent. You'll see a significant slowdown of bud development (as well as overall plant growth), lower bud sites will start to darken and wilt - eventually dying off altogether, and buds may start losing their vibrant color.
During this stage, a phosphorus deficiency can significantly impact yield and potency if not addressed quickly.
Early vs. advanced symptoms of phosphorus deficiency
Phosphorus is a Mobile nutrient, meaning that it can be moved around a plant's body as needed.
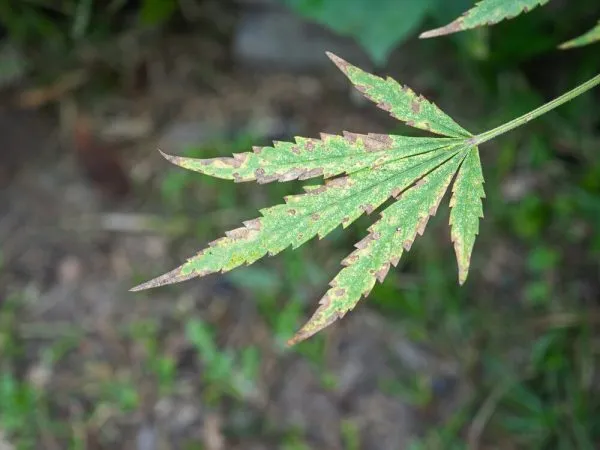
As such, early signs of deficiency will first be seen in the older leaves - the plant will begin to move what it has left of phosphorus to the newer growth that needs it most for crucial processes like cell division and energy production.
The older leaves will first start to lose their vibrant green color, turning a dull and lifeless dark green. They'll also start to develop 'rust spots' (reddish-brown spots). This change of color will also be present in the veins and stems of the leaves. Eventually, these spots will turn into large brown blotches that can most of the leaf, spreading out from the veins with the leaves curling in on themselves downwards.
If left unchecked, as the cells really start to suffer, the overall structure of the plant will start to change - it will become weak and fragile. This leads to a risk of breakages at the stem, making plants more prone to disease.
How phosphorus deficiency differs from other nutrient deficiencies
I've mentioned that some of the signs and symptoms of a phosphorus deficiency can be similar to other deficiencies and issues, such as overwatering.
When it comes to the main 3 nutrients:
- Nitrogen issues will show as yellowing lower leaves.
- Potassium deficiencies will cause the leaves to brown and potentially 'burn' at the tips and edges.
- Phosphorus issues will cause the leaves to darken and wilt (but not burn), with purple/red stems and veins.
Other more common deficiencies, such as magnesium, calcium, and iron, can also show similar signs to a phosphorus deficiency (darkening and wilting of leaves) but not the red/purple coloring in stems and veins.
Fixing phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants
Now that you are sure that a phosphorus deficiency is the issue, it's time to take action and fix the problem.
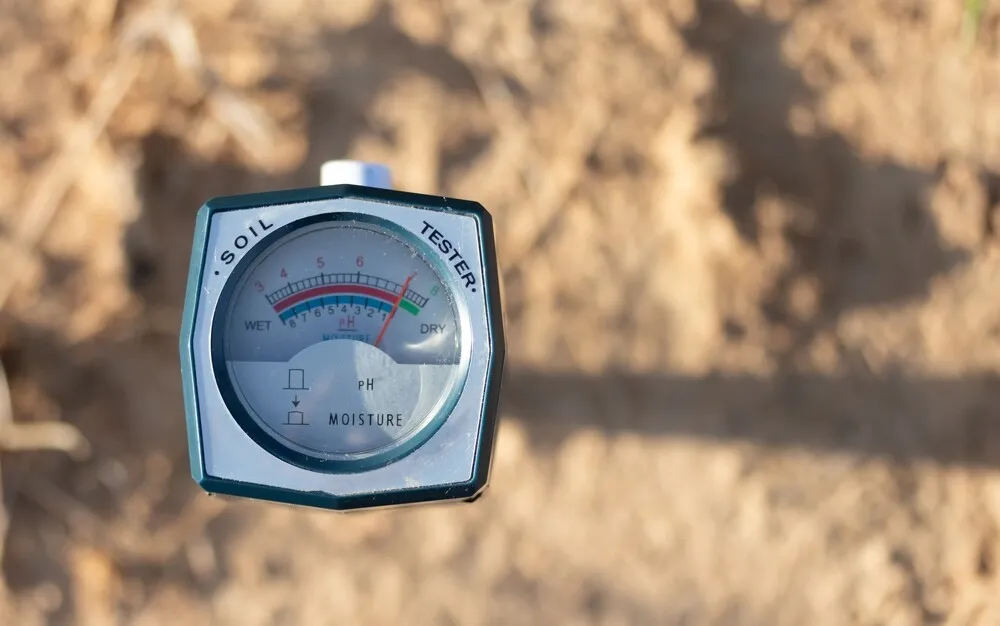

Step-by-step guide to addressing phosphorus-deficient plants
Correcting soil and pH issues
First up, check the pH of the root zone.
If you haven't been using a digital pH pen to monitor and adjust the pH the water/nutrient solution you've been feeding your plants - now's the time to start. pH is a crucial aspect of growing weed, and if it's off balance, one of the first things to suffer will be nutrient uptake.
You can also use the pH meter to test the runoff from your plants, which will give you a decent (but not super accurate) idea of what the pH in your root zone is like. If this is way out, it's time for the next step...
Flush your plants
If the medium's pH is out, you need to flush it with properly pH-balanced water. This process will help wash away any nutrients that are unavailable due to a poor root zone pH and give them a chance to start fresh.
The easiest way to flush is to pour pH'd water through the medium. If you're using a 5-gallon pot, slowly pour double that (10 gallons) through the pot, letting it drain away.
Improve soil aeration and drainage
If it's not a pH issue (or even if it is), the next step is to address any drainage issues your medium might have. You check the drainage and aeration of your medium by digging a small hole in the soil near the roots. If it's clogged with old roots, compacted, or sopping wet, then you've found the problem!
If this is the case, carefully remove as much of the compacted soil as you can without damaging any roots. You can even pull the plant out of its pot to do this if need be. Once removed, wash the roots off VERY CAREFULLY with pH'd water, and repot it with fresh soil that has been suitably aerated and more free-draining.
Increase temperature if too cold
It's best (if possible) to keep your grow room or tent around 68-80°F (20-27°C) for optimal nutrient uptake and plant growth. A simple space heater may be enough to raise the temperature if needed, but make sure to hook this up to a thermostat or timer if you're not around 24/7.
Adjusting nutrient supplements for optimal phosphorus levels

Top up your nutrient levels
If pH and drainage are sorted, and it's warm enough - then it's time to top up the level of phosphorus in your nutrient solution. If you're using a pre-mixed bottled formula, make sure you are using the right one for the stage of growth your plants are in, and the cultivation method you're using (i.e. don't use coco-coir specific nutrients if you're growing in hydro, for example).
If you are going the organic route, you can use bat guano or worm castings to supplement phosphorus levels.
Monitor progress and adjust if needed
After taking the above step, monitor your plants' progress. If the symptoms start to improve and new growth is looking healthy, then you're on the right track. Continue with regular feeding and monitoring of pH levels.
If there are no signs of improvement, then you may need to adjust the nutrient levels further. It's also essential to continue monitoring pH levels regularly and flush more than once if needed.
Preventing phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants

It's such an overused cliché, but it's true - prevention is better than cure. There's no better feeling that making it from seed to harvest with no hiccups, and by just following a few simple steps, you can avoid phosphorus deficiency altogether.
Choosing the right soil / growing medium
This should go without saying, but starting with the right soil or growing medium is about as important as it gets.
Soil growers will do best to either start with a really lovely, rich outdoor soil (if that is available to you). If not, head to your local hydro supply store (or just search online) and grab some high-quality, pre-fertilized, cannabis-specific, pH-balanced potting soil.
Hydro growers need to be equally, if not more, vigilant when it comes to choosing the right growing medium. Coco coir is a great option for beginners because its pH neutral, easy to work with and has excellent water retention capabilities. Clay balls are also a fantastic option, as are pure hydroponic options.
Adjusting pH levels to promote phosphorus absorption
Staying well on top of pH levels is the most important factor in preventing phosphorus deficiency. Ideally, you should aim for a pH level of 6.0-7.0 for soil growers and slightly lower (5.5-6.5) for hydroponic setups.
If you use tap water, make sure to let it sit overnight before adjusting the pH - this not only lets the chlorine dissipate but also allows any dissolved solids to settle (meaning you can more accurately adjust pH).
And if you are adding liquid nutes to your feed water, always do so before you check the pH.
Best practices for nutrient scheduling and balancing
Again, why not just make life a little easier on yourself and buy a pre-mixed nutrient solution designed specifically for cannabis plants?
Not only will this help prevent phosphorus deficiency, but it also takes the guesswork out of balancing your plants' nutritional needs.
If you prefer working organically, then there is a wildly huge range of options to choose from, but good old compost is really all you need. Top-dressing once a month and then watering in carefully with pH'd water is a great way to go.
How much phosphorus do cannabis plants need?
Seedling stage
Not very much at all, and this includes all other nutrients at this stage too. The seed contains all the energy and resources that your little plant needs to get started, so adding anymore is unnecessary and may actually harm it.
I prefer to start all my seeds, no matter if I am growing indoors or out, with organic soil or hydro, in rock wool. This is a sterile medium and helps the seeds pop, giving them a safe and comfortable germination environment.
Vegetative stage
This is when you want to start slowly introducing higher levels of phosphorus into your plants' diet. Make sure they have plenty of nitrogen and a small amount of potassium too. If you are using synthetic bottled nutrients, go a little easy until you see how the plants react - it's always easier to add more than it is to take too much back!
Flowering stage
This is when your plants really bump up their phosphorus requirements. It's essential to keep a close eye on your plants during this stage, as they can quickly show signs of phosphorus deficiency if they are not getting enough in their nutrient solution.
FAQs
What pH level is ideal for phosphorus absorption in cannabis?
6.0–7.0 for soil and 5.5–6.5 for hydroponics to maximize phosphorus uptake.
Can phosphorus deficiency affect cannabis potency?
Yes. A lack of phosphorus can reduce cannabinoid and terpene production, leading to weaker aroma, flavor, and potency.
What are the long-term effects of phosphorus deficiency on cannabis yields?
Smaller buds, weaker plants, and reduced trichome production.