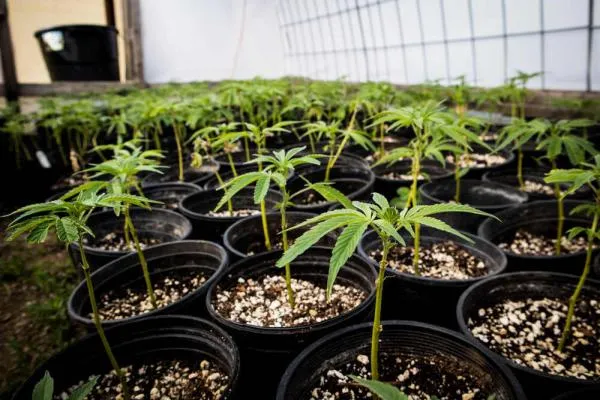
When it comes to growing cannabis, light is the boss – get it wrong and you'll pay the price!
We'll explore what photoperiod means, how it works, and why it's important for plant successful growth. We'll also discuss the different types of photoperiod plants and how to care for them to ensure they thrive. By the end of this article, you'll have a better understanding of cannabis in general and how to use it to your advantage in your garden or indoor plant collection.
- What is a photoperiod cannabis plant?
- Is a Photoperiod the same as Feminized?
- How long do photoperiod plants take to grow?
- Can you make a photoperiod plant grow faster?
- How long should you veg a photoperiod?
- What are the pros and cons of growing photoperiods?
- What are the stages of growth for a photoperiod?
- Tips on how to grow a photoperiod strain
- Photoperiod cannabis FAQ
- Conclusion
What is a photoperiod cannabis plant?
Photoperiod means cannabis plants have two different phases in their life cycle: vegetative growth and bloom. These two periods are controlled by how much light the plant receives and the length of time it receives it. Long days mean vegetative growth, shorter days means flowering time.
When photoperiod cannabis seeds are grown with around 18 hours (or more) of daily light, the plant stays in vegetative growth; which means the plant put its energy into roots, leaves, and branches, but not buds. When the daily light hours are reduced to around 12, flowering begins, and for female plants this means buds.
Look at it this way: in the wild cannabis sprouts in the spring, as the days get longer it know it has the whole of summer ahead of it so it just wants to get bigger. When it hits the summer solstice and the days are at their maximum length it will keep putting on vegetative growth (roots, stems, leaves etc). By mid summer the days are getting shorter and the plants knows it doesn’t have months and months of time left, so it starts to put its energy into reproduction; for weed, this means buds!
Is a Photoperiod the same as Feminized?
No, a photoperiod cannabis plant and a feminized cannabis plant are not the same.
A photoperiod cannabis plant refers to the reliance on changes in the light-dark cycle to trigger its growth and flowering stages. The plant will enter the flowering phase when exposed to a specific light schedule (usually 12 hours of light followed by 12 hours of darkness). This type of cannabis can be either male or female, and it requires differences in light cycles to control its growth and flowering. This means that photoperiod plants can be either male or female as the light cycles are unrelated to gender.
On the other hand, feminized cannabis plants are genetically altered to ensure that they will only produce female flowers. They can be any type of cannabis (photo, autoflower or super auto) but will only become female plants when they are grown.
By using feminized seeds, growers can eliminate the need to identify and remove male plants, which do not produce the desired buds and can potentially pollinate female plants, leading to lower-quality yields.
How long do photoperiod plants take to grow?
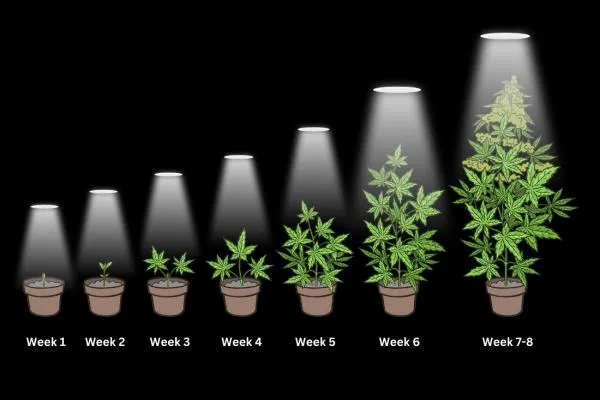
The time it takes for photoperiod cannabis plants to grow can vary depending on several factors, including the specific strain, growing conditions, and desired outcomes. However, to a greater lesser extent, all photoperiod cannabis plants go through the following stages:
- Seedling Stage: This stage typically lasts for 1 to 3 weeks after germination. During this time, the plant focuses on establishing its root system and developing its first few sets of leaves.
- Vegetative Stage: The vegetative stage can last anywhere from 4 to 8 weeks or even longer outdoors, depending on the grower's preference and the desired size of the plant. During this phase, the plant experiences rapid leaf and stem growth, focusing on building its overall structure.
- Flowering Stage: Once the photoperiod plant enters the flowering stage, it will start producing buds. The length of the flowering stage can range from 6 to 14 weeks, depending on the strain and environmental conditions.

In total, from germination to harvest, photoperiod cannabis plants can take anywhere from 10 to 22 weeks or more. It's crucial for growers to monitor their plants closely during each stage, providing them with the appropriate nutrients, light, and care to ensure a successful and bountiful harvest.
Can you make a photoperiod plant grow faster?
While you cannot make a photoperiod cannabis plant grow faster in the sense of altering its biological growth rate, you can employ certain techniques to optimize its growth and potentially reduce the overall time to harvest. Here are some methods to help maximize growth:
- Provide Adequate Light: Ensuring your photoperiod plants receive the right amount of light during the vegetative stage is crucial. High-quality grow lights with the proper spectrum and intensity can encourage faster and healthier growth.
- Optimize Nutrients: Using the right balance of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, will support robust growth during both the vegetative and flowering stages.
- Maintain Ideal Growing Conditions: Keep the growing environment within the ideal temperature and humidity range for cannabis cultivation. This promotes faster growth and reduces the risk of stress-related issues.
- Pruning and Training: By strategically pruning and training the plants, you can encourage better light penetration and airflow, leading to more significant bud development and potentially earlier flowering.
- Healthy Roots, Healthy Plants: Ensure your plants have a well-developed root system by using appropriate pot sizes and proper watering practices. Healthy roots enable better nutrient uptake, supporting overall plant growth.
- Control Light Cycles: Although you can't make the plant grow faster, controlling the light cycle during the flowering stage will affect the total growth time of the plant. Switching to a consistent and uninterrupted 12-hour light/12-hour dark schedule sooner will promote efficient flower development earlier in the overall life of the plant.
- Choose Fast-Flowering Strains: When selecting photoperiod cannabis strains, look for those with shorter flowering times. Some strains are bred to have quicker flowering periods, which can expedite the time to harvest.
It's important to note that while these techniques can optimize growth, cannabis plants still require their natural time to mature fully. Rushing the process excessively could lead to lower-quality yields or other potential issues. Always prioritize plant health and follow best practices to achieve the best results.
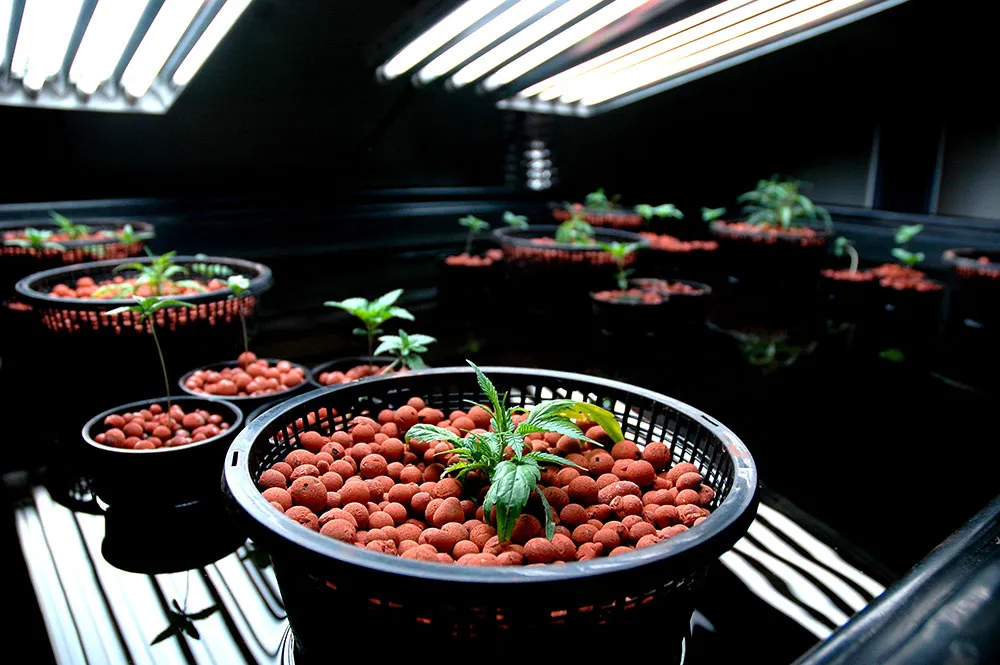

How long should you veg a photoperiod?
The duration of the vegetative (veg) stage for photoperiod cannabis plants can vary based on several factors, including the strain, desired plant size, and available space. On average, the vegetative stage for photoperiod cannabis plants can last anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks.
Here are some general guidelines to consider when deciding how long to veg a photoperiod plant:
- Plant Size: The longer you allow the plant to stay in the vegetative stage, the larger it will grow. If you have sufficient space and want bigger plants, you can extend the vegetative phase.
- Strain Characteristics: Some cannabis strains naturally grow taller and take longer to mature. Understanding the specific traits of the strain you are cultivating can help you determine the appropriate veg time.
- Indoor vs. Outdoor Growing: Indoor growers often keep their plants in the vegetative stage for a shorter period, usually 4 - 6 weeks, due to limited space and the desire to initiate flowering sooner. Outdoor growers allow their plants to veg for longer, as the natural length of the day dictates the amount of sunlight and they frequently have larger growing areas.
- Grower's Preference: Ultimately, the decision on how long to veg a photoperiod plant depends on the grower's goals and preferences. Some may prefer shorter veg times for quicker harvests, while others may opt for longer veg periods to achieve larger yields.
Remember that during the vegetative stage, photoperiod plants focus on developing their structural growth, building a strong root system, and increasing leaf mass. Once you decide to switch to the flowering stage, you need to adjust the light cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness to trigger flowering.
It's essential to monitor your plants regularly and adjust the veg time based on their health and development. Healthy and vigorous plants are more likely to produce better yields during the flowering stage.
What are the pros and cons of growing photoperiods?
Growing photoperiod cannabis plants offers greater control, training possibilities, and potential for larger yielding plants.
However, it requires more time and attention to detail compared to autoflowering strains. The choice between photoperiod and autoflowering varieties depends on the grower's preferences, experience, and specific cultivation goals.
Pros of Growing Photoperiods:
- Control over plant size and structure: Photoperiod plants allow growers to control the growth and development of the plant by training during the vegetative period
- Longer vegetative growth period: Photoperiod plants have a longer vegetative growth period, which allows for greater mass to be laid down by the plant.
- Larger yields: Photoperiod plants can produce larger yields than autoflowering plants.
- Can be used as mother plants: Photoperiod plants can be used as mother plants for many years, and numerous cuttings can be taken from a single plant.
Cons of Growing Photoperiods:
- Longer grow cycle: Photoperiod plants have a longer grow cycle than autoflowering plants, which means it takes longer to harvest.
- Require more maintenance: Photoperiod plants can require more maintenance in the form of pruning and shaping to maximise yields.
- Require a change in light cycle: Photoperiod plants require a change in light cycle to force them to flower, which can be more challenging for novice growers.
What are the stages of growth for a photoperiod?
The growth of a photoperiod cannabis plant typically goes through several distinct stages. These stages are important milestones in the plant's life cycle, each requiring specific care and attention to ensure successful growth. Here are the primary stages:
- Germination: The first stage begins when the seed absorbs water and initiates root and shoot growth. Germination occurs when the seed cracks open, and a taproot emerges.
- Seedling: During this stage, the plant develops its first set of leaves, called cotyledons, and begins to establish its root system. Seedlings are delicate and require a controlled environment with proper humidity and light to thrive.
- Vegetative Stage: In the vegetative stage, the plant focuses on vigorous leaf and stem growth. It develops multiple sets of leaves and branches as it prepares for the flowering phase. This stage lasts anywhere from a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the desired plant size and strain genetics.
- Pre-flowering: Just before entering the flowering stage, photoperiod plants often go through a pre-flowering phase. During this time, the plant will show its sex, allowing growers to identify and remove any male plants to prevent pollination of the females.
- Flowering Stage: The flowering stage is initiated by adjusting the light cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness. During this phase, the plant shifts its focus from vegetative growth to producing buds. The duration of the flowering stage can vary depending on the strain and usually lasts 6 to 14 weeks.
- Harvest: This final stage occurs when the buds have reached their peak maturity and are ready for harvest. The timing of the harvest is essential to achieve the desired potency and effects of the cannabis flowers.
It's important to note that environmental factors, nutrient management, and the grower's care can significantly influence the duration and success of each growth stage. By understanding and providing appropriate conditions for each stage, growers can maximize their yield and produce high-quality cannabis flowers.
Tips on how to grow a photoperiod strain
Growing a photoperiod cannabis strain can be a rewarding experience, and with the right approach, you can achieve successful results. Here are some essential tips to help you grow photoperiod strains effectively:
- Choose the Right Strain: Research and select a photoperiod strain that suits your growing environment, experience level, and desired effects. Consider factors like size, flowering time, and resistance to pests and diseases.
- Provide plenty of Light: Ensure your plants receive sufficient light during the vegetative stage to promote healthy growth. High-quality grow lights with the right spectrum (blue light) and intensity are crucial for robust vegetative development.
- Master Light Cycles: Understand the importance of light cycles for photoperiod plants. During the flowering stage, maintain a consistent 12 hours of light and 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness to initiate and maintain flowering.
- Create the Ideal Growing Environment: Maintain optimal temperature, humidity, and ventilation levels in your grow space. Adequate airflow helps prevent mold and mildew, while the right temperature range (20-28°C or 68-82°F) encourages healthy growth.
- Choose the Right Growing Medium: Whether you opt for soil, coco coir, or hydroponics, ensure the growing medium provides adequate nutrients and proper drainage for healthy root development.
- Nutrient Management: Understand the nutrient needs of your plants during each growth stage. Avoid overfeeding, as this can lead to nutrient imbalances or nutrient burn. Follow a nutrient feeding schedule suitable for your chosen growing medium.
- Training Techniques: Consider using training techniques such as topping, low-stress training (LST), or scrogging to encourage bushier growth and increase light penetration to lower bud sites.
- Monitor pH Levels: Regularly check and adjust the pH of your nutrient solution to ensure proper nutrient uptake by the plants. The recommended pH range is typically around 5.5 to 6.5 for soil and hydroponic setups.
- Prune and Defoliate: Remove any dead or yellowing leaves and strategically prune the plant to improve airflow and light distribution. However, avoid excessive defoliation during the flowering stage, as it can stress the plant.
- Monitor Plant Health: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies. Catching and addressing issues early can prevent them from becoming more significant problems.
- Be Patient and Observant: Cannabis cultivation requires patience and attention to detail. Observe your plants closely, and adapt your care based on their specific needs and growth patterns.
Remember that growing cannabis is a learning process, and each strain may have unique requirements. Stay open to experimenting and adapting your techniques to find what works best for your specific photoperiod strain and growing environment.
Photoperiod cannabis FAQ
Are photoperiods more potent?
The potency of cannabis depends on the strain and its cannabinoid profile rather than whether it is photoperiod or autoflowering. Both types can have high potency depending on the genetics and how well they are grown.
When should you top a photoperiod plant?
You can top a photoperiod cannabis plant during the vegetative stage, usually after it has developed 3-4 sets of leaves. This encourages lateral growth and creates a bushier plant.
Do photoperiod yield more than autoflowers?
Generally, photoperiod cannabis plants have the potential to yield more than autoflowers due to their longer vegetative stage, which allows them to grow larger and develop more bud sites. However, it depends on the specific strain and the growing conditions.
Conclusion
Photoperiod plants are those whose flowering cycle is determined by the light/dark ratio they receive. Understanding this crucial aspect empowers growers to manipulate their plants' flowering times effectively.
Remember, adjusting light schedules can be a game-changer for your next grow! Now you're ready to optimize your yields and harvests. Don't forget to like and share this article to spread the knowledge and help fellow growers! Happy growing!